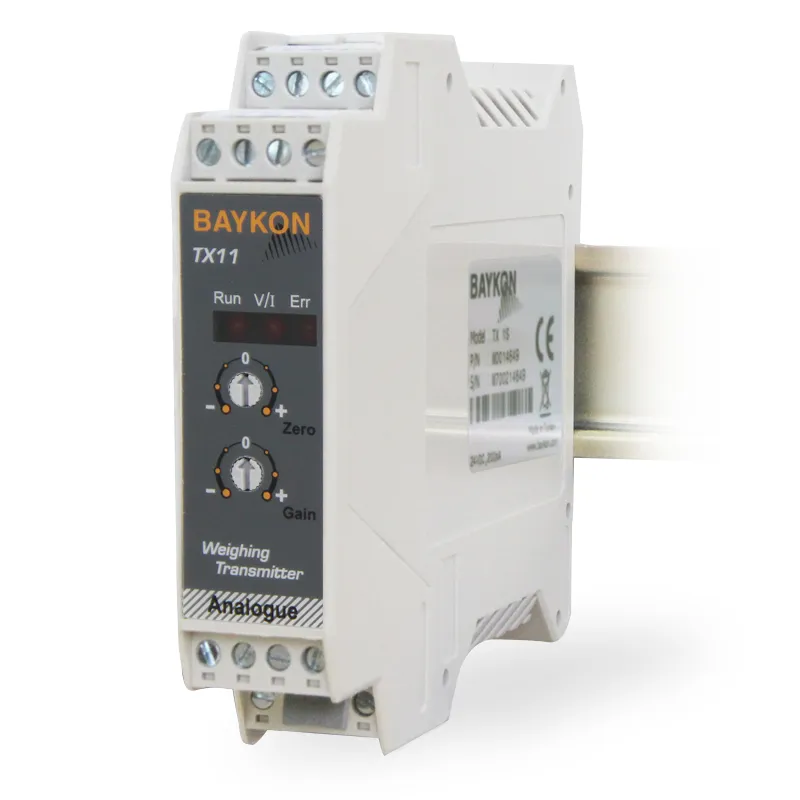
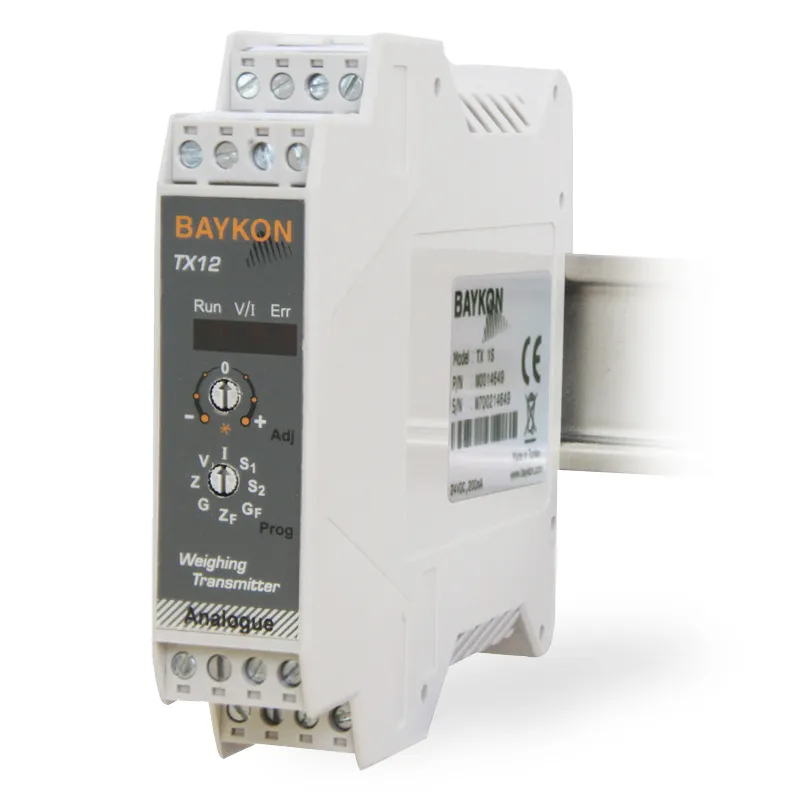
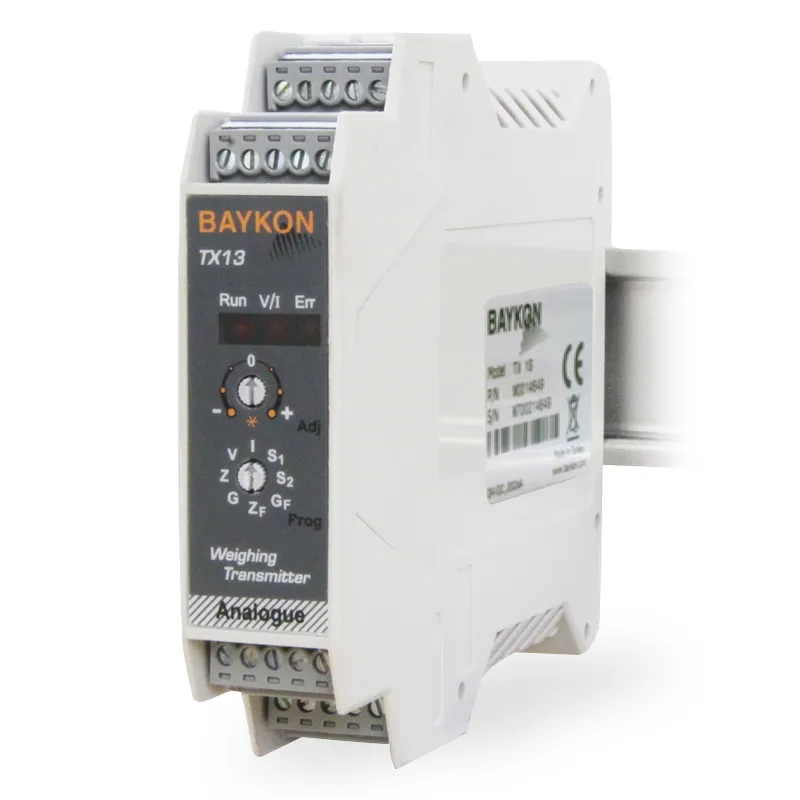
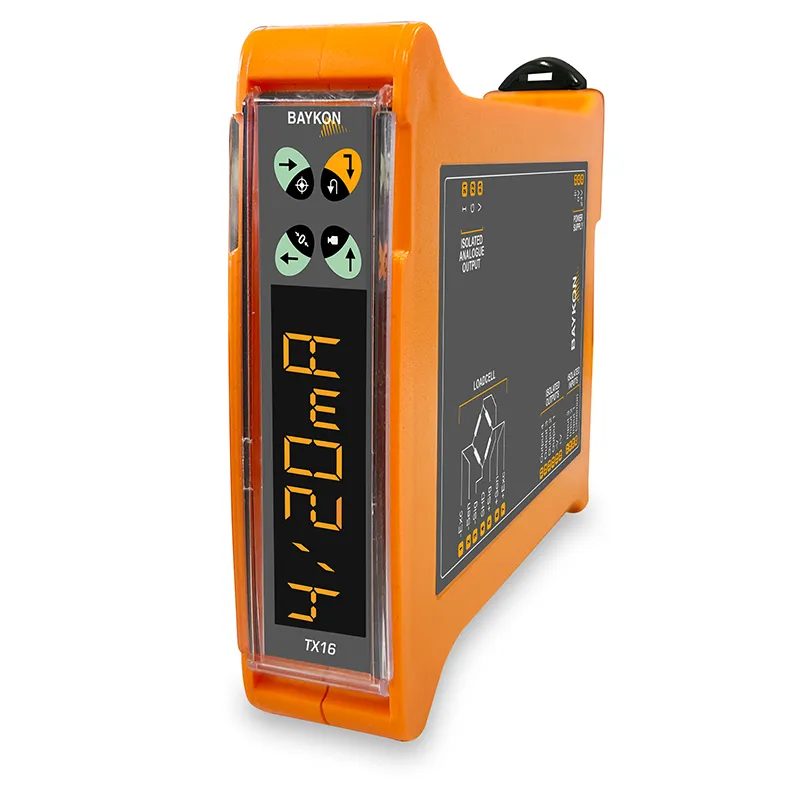
Analogue Transmitters
What is an Analog Transmitter?
An analog transmitter is a device that converts a physical quantity (such as weight, pressure, temperature) into an electrical signal. They are widely used in industrial automation and control systems. These devices typically produce standard electrical signals like 4-20 mA or 0-10 V. By providing precise measurements, analog transmitters enable the monitoring and control of production processes. Supplying accurate and reliable data is critical for the effectiveness of industrial processes.
How Does an Analog Transmitter Work?
Analog transmitters operate by working with a load cell or a similar sensor. The process generally consists of the following steps:
◦ Load Cell: Senses a physical load and produces voltage changes.
◦ Signal Conversion: The voltage from the load cell is converted into an electrical signal by the analog transmitter.
◦ Data Transmission: The generated electrical signal is transmitted to a control system or user interface, allowing real-time data monitoring.
Types of Analog Transmitters
Analog transmitters come in different types based on their applications and needs. Some types include:
◦ Weight Transmitter: Directly measures physical weight and is used in automatic weighing systems.
◦ Pressure Transmitter: Measures the pressure of gases or liquids and transmits these values as electrical signals.
◦ Temperature Transmitter: Performs temperature measurements and transfers results to analytical systems.
◦ Speed Transmitter: Used to measure the movement speed of an object and send data to control systems.
Applications of Analog Transmitters
Analog transmitters are used in various industrial applications, including:
◦ Tank Weighing: Used to measure the weight of liquids or solids in tanks.
◦ Silo Weighing: A critical tool in the agricultural sector for determining the amount of grain and other materials.
◦ Tensile and Compression Testing: Used in material durability tests and quality control processes.
◦ Process Control: Essential for monitoring and controlling processes in industrial automation systems.
◦ Tension Measurement Systems: Used to monitor the tension in structures and machines.
Selecting an Analog Transmitter
When selecting an analog transmitter, several important factors should be considered:
◦ Measurement Range: The required measurement range should be determined. It’s essential to choose a device that can withstand overload conditions.
◦ Operating Conditions: Consider the temperature, pressure, and other physical conditions of the environment where the device will be used.
◦ Output Type: Determine the type of electrical output needed (4-20 mA, 0-10 V, etc.).
◦ Accuracy: Consider the level of accuracy required for the application.
Calibration of Analog Transmitters
Regular calibration is necessary for analog transmitters to function accurately. Calibration ensures the accuracy of the device’s measurement results and typically includes the following steps:
◦ Reference Measurement: The device to be calibrated is compared with a reference measuring device.
◦ Adjustment: Measurement results are aligned with reference values.
◦ Documentation: The calibration process is documented, and periodic checks are scheduled.